redis源码学习-rax篇
0 条评论redis源码学习-rax篇
rax介绍
rax为redis自实现的基数树,从构造上讲,也叫前缀树/前缀压缩树。用来作为stream的底层数据结构之一,在redis5中引入。
rax结构分析
rax在内存中为顺序结构,但可以转化为树形结构方便理解
rax中保存数据有两种格式,一种是非压缩的格式,另一种为压缩的格式。
以为源码中注释为例,假设有foo footer foobar三个单词,
在非压缩的格式下,树形结构如下示例
(f) “”
\
(o) “f”
\
(o) “fo”
\
[t b] “foo”
/ \
“foot” (e) (a) “foob”
/ \
“foote” ® ® “fooba”
/ \
“footer” [] [] “foobar”
可以看到,每个节点中只保留一个字符。footer与foobar相同前缀为foo,那么以单个字符开始构造,到分歧处已经形成三级节点。
在压缩格式下,树形结构如下示例
[“foo”] “”
|
[t b] “foo”
/ \
“foot” (“er”) (“ar”) “foob”
/ \
“footer” [] [] “foobar”
每个节点中保留字符串,通常为当前分歧中的最大公共前缀。 footer与foobar公共的foo单占一个节点,到分歧处只有一级节点,
回到代码,先看rax长什么样
raxnode
#define RAX_NODE_MAX_SIZE ((1<<29)-1)
typedef struct raxNode {
uint32_t iskey:1; /* Does this node contain a key? */
uint32_t isnull:1; /* Associated value is NULL (don't store it). */
uint32_t iscompr:1; /* Node is compressed. */
uint32_t size:29; /* Number of children, or compressed string len. */
/* Data layout is as follows:
*
* If node is not compressed we have 'size' bytes, one for each children
* character, and 'size' raxNode pointers, point to each child node.
* Note how the character is not stored in the children but in the
* edge of the parents:
*
* [header iscompr=0][abc][a-ptr][b-ptr][c-ptr](value-ptr?)
*
* if node is compressed (iscompr bit is 1) the node has 1 children.
* In that case the 'size' bytes of the string stored immediately at
* the start of the data section, represent a sequence of successive
* nodes linked one after the other, for which only the last one in
* the sequence is actually represented as a node, and pointed to by
* the current compressed node.
*
* [header iscompr=1][xyz][z-ptr](value-ptr?)
*
* Both compressed and not compressed nodes can represent a key
* with associated data in the radix tree at any level (not just terminal
* nodes).
*
* If the node has an associated key (iskey=1) and is not NULL
* (isnull=0), then after the raxNode pointers pointing to the
* children, an additional value pointer is present (as you can see
* in the representation above as "value-ptr" field).
*/
unsigned char data[];
} raxNode;
- iskey 表示当前节点是否是一个完整的key,如果当前节点是完整的key,那么才会保存相对应的value
- isnull 表示当前节点对应的value是否为null,前提是iskey为1,否则不用看这个字段
- iscompr 表示当前节点是否为压缩节点。之前用两个图示表明压缩与非压缩的区别,
- size 假如当前节点为压缩节点,那么这个字段保存的是压缩字符串的长度。如果是非压缩节点,那么这个字段保存的是子节点的个数
- data 用来保存对应的字符串,同时指向子节点,如果是当前节点是key的话那么指向value,为指针。
看宏定义中的RAX_NODE_MAX_SIZE,表明rax自身支持的数据量大小,所以一个raxnode的header长度就固定下来(iskey,isnull.iscompr,.size)
如下图式带数据结构下的foo foobar与footer - 对于非压缩格式
先插入foo
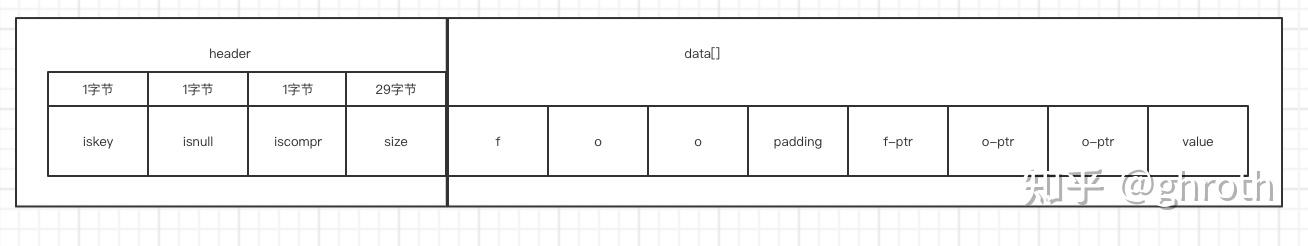
再插入foobar
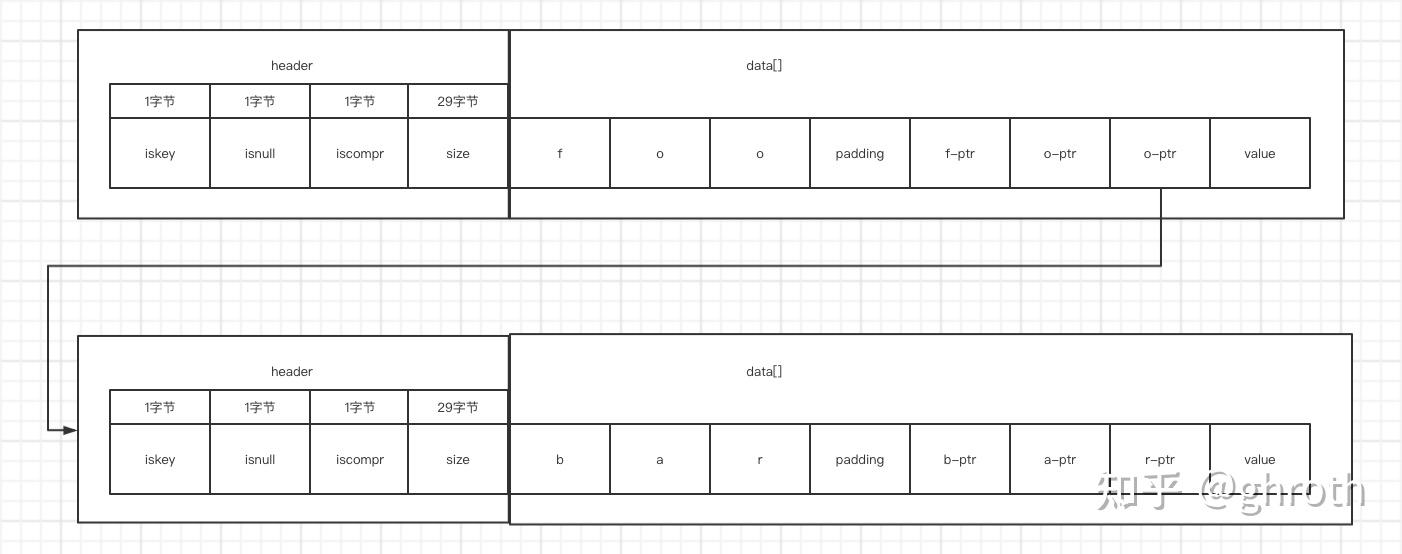
再插入footer
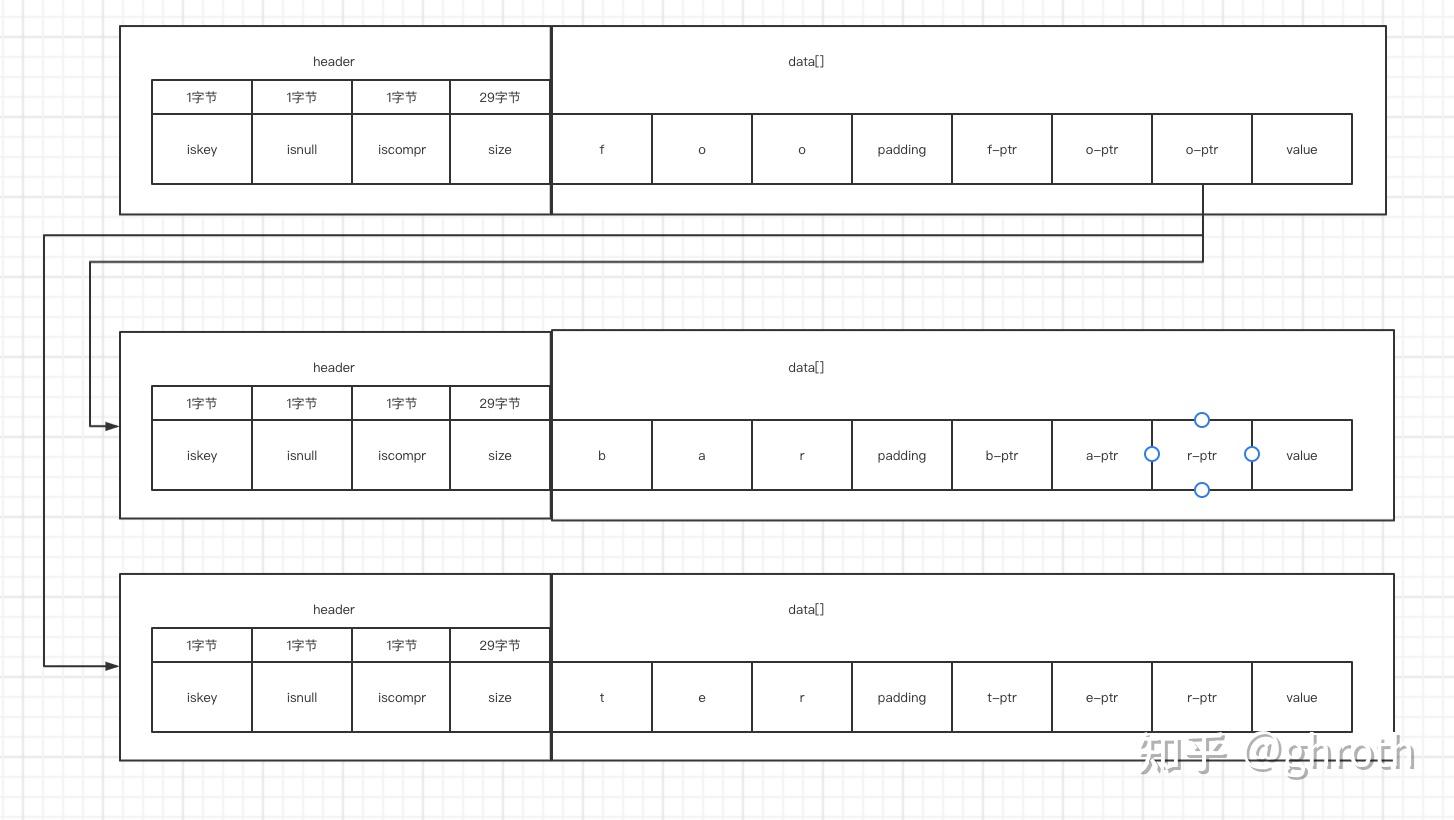
就形成了这个结构 - 对于压缩格式
直接给出三个单词插入后的最终图
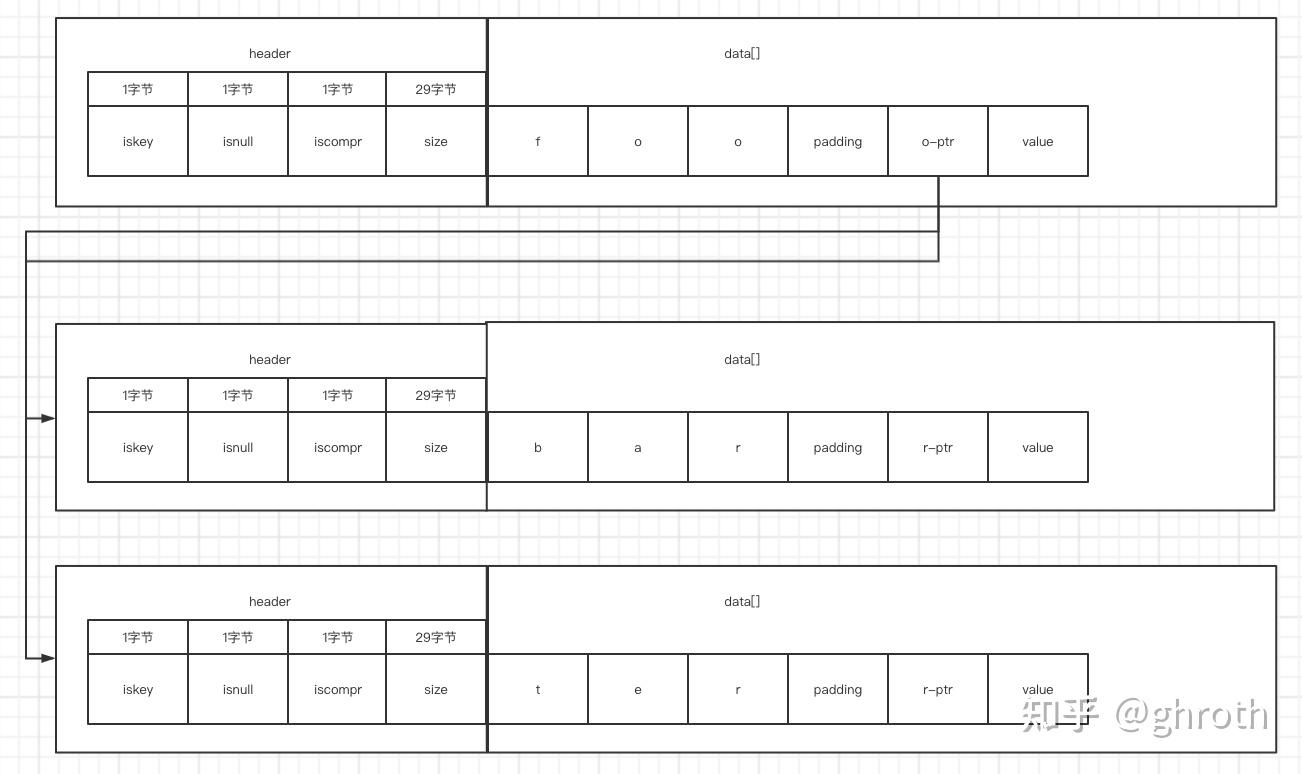
对比压缩格式与非压缩格式,其实从构造上看没什么大的区别,对于foo来说,压缩后只有o-ptr,而非压缩会有f-ptr,o-ptr,o-ptr的区别
其中,每个-ptr如果不指向子节点,都需要指向一个只含有value的raxnode,图中限于图片大小全部省略掉了。*
padding为预留字段,为了保证字节对齐,会用padding来补充对齐不足的位数
当读懂了如上图示,那么rax整体在redis中的处理基本上就有了轮廓了。
rax
typedef struct rax {
raxNode *head;
uint64_t numele;
uint64_t numnodes;
} rax;
rax就是rax整体的入口了。记录raxnode头,numele为元素的数量,numnodes为节点数量。由于raxnode的构造,大多数rax的numele >= numnodes。
rax源码分析
raxNew
rax *raxNew(void) {
//rax_malloc本质上还是malloc
rax *rax = rax_malloc(sizeof(*rax));
if (rax == NULL) return NULL;
rax->numele = 0;
//空的头节点也占numnodes数
rax->numnodes = 1;
rax->head = raxNewNode(0,0);
if (rax->head == NULL) {
rax_free(rax);
return NULL;
} else {
return rax;
}
}
raxInsert
int raxInsert(rax *rax, unsigned char *s, size_t len, void *data, void **old) {
return raxGenericInsert(rax,s,len,data,old,1);
}
/* Insert the element 's' of size 'len', setting as auxiliary data
* the pointer 'data'. If the element is already present, the associated
* data is updated (only if 'overwrite' is set to 1), and 0 is returned,
* otherwise the element is inserted and 1 is returned. On out of memory the
* function returns 0 as well but sets errno to ENOMEM, otherwise errno will
* be set to 0.
*/
int raxGenericInsert(rax *rax, unsigned char *s, size_t len, void *data, void **old, int overwrite) {
size_t i;
int j = 0; /* Split position. If raxLowWalk() stops in a compressed
node, the index 'j' represents the char we stopped within the
compressed node, that is, the position where to split the
node for insertion. */
raxNode *h, **parentlink;
debugf("### Insert %.*s with value %p\n", (int)len, s, data);
//找寻最优存放节点位置
//j用来记录分裂的位置,因为c没有go一样的多返回值设计,所以在这里使用指针代替多返回值,通过一个函数拿到i j两个值的结果
i = raxLowWalk(rax,s,len,&h,&parentlink,&j,NULL);
/* If i == len we walked following the whole string. If we are not
* in the middle of a compressed node, the string is either already
* inserted or this middle node is currently not a key, but can represent
* our key. We have just to reallocate the node and make space for the
* data pointer. */
//假如i==len,那么说明整个遍历了一遍
//如果当前节点为非压缩节点,且没有找到分裂位置,那么就说明这个字符串已经存在或者是个非元素节点
if (i == len && (!h->iscompr || j == 0 /* not in the middle if j is 0 */)) {
debugf("### Insert: node representing key exists\n");
/* Make space for the value pointer if needed. */
//如果不是key,需要重新分配节点空间,更新指针位置
if (!h->iskey || (h->isnull && overwrite)) {
h = raxReallocForData(h,data);
if (h) memcpy(parentlink,&h,sizeof(h));
}
if (h == NULL) {
errno = ENOMEM;
return 0;
}
/* Update the existing key if there is already one. */
//如果是key,那么说明当前字符串已经存在,需要设置新的value
if (h->iskey) {
if (old) *old = raxGetData(h);
if (overwrite) raxSetData(h,data);
errno = 0;
return 0; /* Element already exists. */
}
/* Otherwise set the node as a key. Note that raxSetData()
* will set h->iskey. */
//说明键也不存在,需要set键值对
raxSetData(h,data);
rax->numele++;
return 1; /* Element inserted. */
}
/* If the node we stopped at is a compressed node, we need to
* split it before to continue.
*
* Splitting a compressed node have a few possible cases.
* Imagine that the node 'h' we are currently at is a compressed
* node containing the string "ANNIBALE" (it means that it represents
* nodes A -> N -> N -> I -> B -> A -> L -> E with the only child
* pointer of this node pointing at the 'E' node, because remember that
* we have characters at the edges of the graph, not inside the nodes
* themselves.
*
* In order to show a real case imagine our node to also point to
* another compressed node, that finally points at the node without
* children, representing 'O':
*
* "ANNIBALE" -> "SCO" -> []
*
* When inserting we may face the following cases. Note that all the cases
* require the insertion of a non compressed node with exactly two
* children, except for the last case which just requires splitting a
* compressed node.
*
* 1) Inserting "ANNIENTARE"
*
* |B| -> "ALE" -> "SCO" -> []
* "ANNI" -> |-|
* |E| -> (... continue algo ...) "NTARE" -> []
*
* 2) Inserting "ANNIBALI"
*
* |E| -> "SCO" -> []
* "ANNIBAL" -> |-|
* |I| -> (... continue algo ...) []
*
* 3) Inserting "AGO" (Like case 1, but set iscompr = 0 into original node)
*
* |N| -> "NIBALE" -> "SCO" -> []
* |A| -> |-|
* |G| -> (... continue algo ...) |O| -> []
*
* 4) Inserting "CIAO"
*
* |A| -> "NNIBALE" -> "SCO" -> []
* |-|
* |C| -> (... continue algo ...) "IAO" -> []
*
* 5) Inserting "ANNI"
*
* "ANNI" -> "BALE" -> "SCO" -> []
*
* The final algorithm for insertion covering all the above cases is as
* follows.
*
* ============================= ALGO 1 =============================
*
* For the above cases 1 to 4, that is, all cases where we stopped in
* the middle of a compressed node for a character mismatch, do:
*
* Let $SPLITPOS be the zero-based index at which, in the
* compressed node array of characters, we found the mismatching
* character. For example if the node contains "ANNIBALE" and we add
* "ANNIENTARE" the $SPLITPOS is 4, that is, the index at which the
* mismatching character is found.
*
* 1. Save the current compressed node $NEXT pointer (the pointer to the
* child element, that is always present in compressed nodes).
*
* 2. Create "split node" having as child the non common letter
* at the compressed node. The other non common letter (at the key)
* will be added later as we continue the normal insertion algorithm
* at step "6".
*
* 3a. IF $SPLITPOS == 0:
* Replace the old node with the split node, by copying the auxiliary
* data if any. Fix parent's reference. Free old node eventually
* (we still need its data for the next steps of the algorithm).
*
* 3b. IF $SPLITPOS != 0:
* Trim the compressed node (reallocating it as well) in order to
* contain $splitpos characters. Change child pointer in order to link
* to the split node. If new compressed node len is just 1, set
* iscompr to 0 (layout is the same). Fix parent's reference.
*
* 4a. IF the postfix len (the length of the remaining string of the
* original compressed node after the split character) is non zero,
* create a "postfix node". If the postfix node has just one character
* set iscompr to 0, otherwise iscompr to 1. Set the postfix node
* child pointer to $NEXT.
*
* 4b. IF the postfix len is zero, just use $NEXT as postfix pointer.
*
* 5. Set child[0] of split node to postfix node.
*
* 6. Set the split node as the current node, set current index at child[1]
* and continue insertion algorithm as usually.
*
* ============================= ALGO 2 =============================
*
* For case 5, that is, if we stopped in the middle of a compressed
* node but no mismatch was found, do:
*
* Let $SPLITPOS be the zero-based index at which, in the
* compressed node array of characters, we stopped iterating because
* there were no more keys character to match. So in the example of
* the node "ANNIBALE", adding the string "ANNI", the $SPLITPOS is 4.
*
* 1. Save the current compressed node $NEXT pointer (the pointer to the
* child element, that is always present in compressed nodes).
*
* 2. Create a "postfix node" containing all the characters from $SPLITPOS
* to the end. Use $NEXT as the postfix node child pointer.
* If the postfix node length is 1, set iscompr to 0.
* Set the node as a key with the associated value of the new
* inserted key.
*
* 3. Trim the current node to contain the first $SPLITPOS characters.
* As usually if the new node length is just 1, set iscompr to 0.
* Take the iskey / associated value as it was in the original node.
* Fix the parent's reference.
*
* 4. Set the postfix node as the only child pointer of the trimmed
* node created at step 1.
*/
/* ------------------------- ALGORITHM 1 --------------------------- */
//如果是压缩节点的话,并且没有整个遍历一遍,说明需要找分裂节点了
if (h->iscompr && i != len) {
debugf("ALGO 1: Stopped at compressed node %.*s (%p)\n",
h->size, h->data, (void*)h);
debugf("Still to insert: %.*s\n", (int)(len-i), s+i);
debugf("Splitting at %d: '%c'\n", j, ((char*)h->data)[j]);
debugf("Other (key) letter is '%c'\n", s[i]);
/* 1: Save next pointer. */
//获取最后一个子节点的位置
raxNode **childfield = raxNodeLastChildPtr(h);
//用来做数据保存使用的
raxNode *next;
memcpy(&next,childfield,sizeof(next));
debugf("Next is %p\n", (void*)next);
debugf("iskey %d\n", h->iskey);
if (h->iskey) {
debugf("key value is %p\n", raxGetData(h));
}
/* Set the length of the additional nodes we will need. */
//trimmedlen用来计算len使用
size_t trimmedlen = j;
size_t postfixlen = h->size - j - 1;
int split_node_is_key = !trimmedlen && h->iskey && !h->isnull;
size_t nodesize;
/* 2: Create the split node. Also allocate the other nodes we'll need
* ASAP, so that it will be simpler to handle OOM. */
//创建新的raxnode节点
raxNode *splitnode = raxNewNode(1, split_node_is_key);
raxNode *trimmed = NULL;
raxNode *postfix = NULL;
//如果停留在raxnode的中间,那么需要将原节点前面部分字符串转化成新节点的长度
if (trimmedlen) {
nodesize = sizeof(raxNode)+trimmedlen+raxPadding(trimmedlen)+
sizeof(raxNode*);
if (h->iskey && !h->isnull) nodesize += sizeof(void*);
trimmed = rax_malloc(nodesize);
}
//与trimmedlen相反,将原节点后面部分字符串转化成新节点的长度
if (postfixlen) {
nodesize = sizeof(raxNode)+postfixlen+raxPadding(postfixlen)+
sizeof(raxNode*);
postfix = rax_malloc(nodesize);
}
/* OOM? Abort now that the tree is untouched. */
//redis中少见的内存分配异常处理,oom的话需要回滚操作,释放内存
if (splitnode == NULL ||
(trimmedlen && trimmed == NULL) ||
(postfixlen && postfix == NULL))
{
rax_free(splitnode);
rax_free(trimmed);
rax_free(postfix);
errno = ENOMEM;
return 0;
}
//赋予数据
splitnode->data[0] = h->data[j];
//j==0,代表者不再压缩节点中,需要用分裂节点代替原先的节点位置
if (j == 0) {
/* 3a: Replace the old node with the split node. */
if (h->iskey) {
void *ndata = raxGetData(h);
raxSetData(splitnode,ndata);
}
memcpy(parentlink,&splitnode,sizeof(splitnode));
} else {
//如果在压缩节点中,需要分裂压缩节点
/* 3b: Trim the compressed node. */
trimmed->size = j;
//需要将前缀拷贝到新子节点中
memcpy(trimmed->data,h->data,j);
trimmed->iscompr = j > 1 ? 1 : 0;
trimmed->iskey = h->iskey;
trimmed->isnull = h->isnull;
if (h->iskey && !h->isnull) {
void *ndata = raxGetData(h);
raxSetData(trimmed,ndata);
}
// 获取新子节点的最后一个子节点的指针,并且赋予分裂节点的值,将当前新子节点的值赋给父节点,让父节点指向现在的新子节点
raxNode **cp = raxNodeLastChildPtr(trimmed);
memcpy(cp,&splitnode,sizeof(splitnode));
memcpy(parentlink,&trimmed,sizeof(trimmed));
parentlink = cp; /* Set parentlink to splitnode parent. */
rax->numnodes++;
}
/* 4: Create the postfix node: what remains of the original
* compressed node after the split. */
//上边只是创建了新的前缀节点,这里需要创建新的后缀节点
if (postfixlen) {
/* 4a: create a postfix node. */
postfix->iskey = 0;
postfix->isnull = 0;
postfix->size = postfixlen;
postfix->iscompr = postfixlen > 1;
memcpy(postfix->data,h->data+j+1,postfixlen);
raxNode **cp = raxNodeLastChildPtr(postfix);
memcpy(cp,&next,sizeof(next));
rax->numnodes++;
} else {
/* 4b: just use next as postfix node. */
postfix = next;
}
/* 5: Set splitnode first child as the postfix node. */
//获取分裂节点最后一个子节点
raxNode **splitchild = raxNodeLastChildPtr(splitnode);
//postfix指向子节点
memcpy(splitchild,&postfix,sizeof(postfix));
/* 6. Continue insertion: this will cause the splitnode to
* get a new child (the non common character at the currently
* inserted key). */
//h已经无用,释放
rax_free(h);
h = splitnode;
} else if (h->iscompr && i == len) {
//待查找节点的键在压缩节点中被匹配到,那么仍然需要裁剪压缩节点
/* ------------------------- ALGORITHM 2 --------------------------- */
debugf("ALGO 2: Stopped at compressed node %.*s (%p) j = %d\n",
h->size, h->data, (void*)h, j);
/* Allocate postfix & trimmed nodes ASAP to fail for OOM gracefully. */
size_t postfixlen = h->size - j;
size_t nodesize = sizeof(raxNode)+postfixlen+raxPadding(postfixlen)+
sizeof(raxNode*);
if (data != NULL) nodesize += sizeof(void*);
raxNode *postfix = rax_malloc(nodesize);
nodesize = sizeof(raxNode)+j+raxPadding(j)+sizeof(raxNode*);
if (h->iskey && !h->isnull) nodesize += sizeof(void*);
raxNode *trimmed = rax_malloc(nodesize);
if (postfix == NULL || trimmed == NULL) {
rax_free(postfix);
rax_free(trimmed);
errno = ENOMEM;
return 0;
}
/* 1: Save next pointer. */
//保存原先子节点的入口
raxNode **childfield = raxNodeLastChildPtr(h);
raxNode *next;
memcpy(&next,childfield,sizeof(next));
/* 2: Create the postfix node. */
//创建新的后缀节点
postfix->size = postfixlen;
postfix->iscompr = postfixlen > 1;
postfix->iskey = 1;
postfix->isnull = 0;
memcpy(postfix->data,h->data+j,postfixlen);
raxSetData(postfix,data);
raxNode **cp = raxNodeLastChildPtr(postfix);
memcpy(cp,&next,sizeof(next));
rax->numnodes++;
/* 3: Trim the compressed node. */
//裁剪原先的压缩节点
trimmed->size = j;
trimmed->iscompr = j > 1;
trimmed->iskey = 0;
trimmed->isnull = 0;
memcpy(trimmed->data,h->data,j);
memcpy(parentlink,&trimmed,sizeof(trimmed));
//如果原先压缩节点为key,那么新的需要保持一致
if (h->iskey) {
void *aux = raxGetData(h);
raxSetData(trimmed,aux);
}
/* Fix the trimmed node child pointer to point to
* the postfix node. */
//做指针重新指定,
cp = raxNodeLastChildPtr(trimmed);
memcpy(cp,&postfix,sizeof(postfix));
/* Finish! We don't need to continue with the insertion
* algorithm for ALGO 2. The key is already inserted. */
rax->numele++;
rax_free(h);
return 1; /* Key inserted. */
}
/* We walked the radix tree as far as we could, but still there are left
* chars in our string. We need to insert the missing nodes. */
//上述代码是在rax中找到了匹配,这里处理没有匹配的情况,如果匹配之后仍然生下来部分没有匹配到的,需要单独处理
while(i < len) {
raxNode *child;
/* If this node is going to have a single child, and there
* are other characters, so that that would result in a chain
* of single-childed nodes, turn it into a compressed node. */
//假如说当前的节点有一个子节点和其他的字符,那么可以转换成压缩节点,减少一个单一字符子节点
if (h->size == 0 && len-i > 1) {
debugf("Inserting compressed node\n");
size_t comprsize = len-i;
if (comprsize > RAX_NODE_MAX_SIZE)
comprsize = RAX_NODE_MAX_SIZE;
raxNode *newh = raxCompressNode(h,s+i,comprsize,&child);
if (newh == NULL) goto oom;
h = newh;
memcpy(parentlink,&h,sizeof(h));
parentlink = raxNodeLastChildPtr(h);
i += comprsize;
} else {
//如果只有一个字符的节点或者是个非空节点,需要添加子节点
debugf("Inserting normal node\n");
raxNode **new_parentlink;
raxNode *newh = raxAddChild(h,s[i],&child,&new_parentlink);
if (newh == NULL) goto oom;
h = newh;
memcpy(parentlink,&h,sizeof(h));
parentlink = new_parentlink;
i++;
}
rax->numnodes++;
//做迭代
h = child;
}
//保存新节点的数据
raxNode *newh = raxReallocForData(h,data);
if (newh == NULL) goto oom;
h = newh;
if (!h->iskey) rax->numele++;
raxSetData(h,data);
memcpy(parentlink,&h,sizeof(h));
return 1; /* Element inserted. */
oom:
/* This code path handles out of memory after part of the sub-tree was
* already modified. Set the node as a key, and then remove it. However we
* do that only if the node is a terminal node, otherwise if the OOM
* happened reallocating a node in the middle, we don't need to free
* anything. */
if (h->size == 0) {
h->isnull = 1;
h->iskey = 1;
rax->numele++; /* Compensate the next remove. */
assert(raxRemove(rax,s,i,NULL) != 0);
}
errno = ENOMEM;
return 0;
}
从插入节点来说,整体复杂度在O(n^2)以内,但是由于涉及情况比较多,需同时判断压缩与非压缩结构,是否做分裂处理,叶子节点的合并等等,导致代码中夹杂着大量的if分支,使得代码阅读较为难受,但核心思路不变,还是以创建图示的结构为最终目标,其中insert也无特殊技巧读懂逻辑即可。
raxRemove
int raxRemove(rax *rax, unsigned char *s, size_t len, void **old) {
raxNode *h;
raxStack ts;
debugf("### Delete: %.*s\n", (int)len, s);
raxStackInit(&ts);
int splitpos = 0;
size_t i = raxLowWalk(rax,s,len,&h,NULL,&splitpos,&ts);
//没有匹配到字符串或者字符串不是一个键,那么无需操作直接返回即可
if (i != len || (h->iscompr && splitpos != 0) || !h->iskey) {
raxStackFree(&ts);
return 0;
}
//冗余下原值
if (old) *old = raxGetData(h);
h->iskey = 0;
rax->numele--;
/* If this node has no children, the deletion needs to reclaim the
* no longer used nodes. This is an iterative process that needs to
* walk the three upward, deleting all the nodes with just one child
* that are not keys, until the head of the rax is reached or the first
* node with more than one child is found. */
int trycompress = 0; /* Will be set to 1 if we should try to optimize the
tree resulting from the deletion. */
//找到的目的节点没有任何子节点,那么只需要删除当前节点且父节点指针初始化即可
if (h->size == 0) {
debugf("Key deleted in node without children. Cleanup needed.\n");
raxNode *child = NULL;
//如果不是头节点的话,需要向上遍历依次删除
while(h != rax->head) {
child = h;
debugf("Freeing child %p [%.*s] key:%d\n", (void*)child,
(int)child->size, (char*)child->data, child->iskey);
//释放当前节点
rax_free(child);
rax->numnodes--;
h = raxStackPop(&ts);
/* If this node has more then one child, or actually holds
* a key, stop here. */
//如果父节点为key或者父节点还有其他子节点,那么结束循环直接跳出即可
if (h->iskey || (!h->iscompr && h->size != 1)) break;
}
if (child) {
debugf("Unlinking child %p from parent %p\n",
(void*)child, (void*)h);
raxNode *new = raxRemoveChild(h,child);
//需重新分配地址
if (new != h) {
raxNode *parent = raxStackPeek(&ts);
raxNode **parentlink;
if (parent == NULL) {
parentlink = &rax->head;
} else {
parentlink = raxFindParentLink(parent,h);
}
memcpy(parentlink,&new,sizeof(new));
}
/* If after the removal the node has just a single child
* and is not a key, we need to try to compress it. */
//如果移除的节点只有一个子节点并且不是一个键,需要尝试压缩
if (new->size == 1 && new->iskey == 0) {
trycompress = 1;
h = new;
}
}
} else if (h->size == 1) {
/* If the node had just one child, after the removal of the key
* further compression with adjacent nodes is potentially possible. */
//如果这个节点只有一个孩子,那么也需要尝试压缩
trycompress = 1;
}
/* Don't try node compression if our nodes pointers stack is not
* complete because of OOM while executing raxLowWalk() */
//假如会出现oom,撤销压缩操作
if (trycompress && ts.oom) trycompress = 0;
/* Recompression: if trycompress is true, 'h' points to a radix tree node
* that changed in a way that could allow to compress nodes in this
* sub-branch. Compressed nodes represent chains of nodes that are not
* keys and have a single child, so there are two deletion events that
* may alter the tree so that further compression is needed:
*
* 1) A node with a single child was a key and now no longer is a key.
* 2) A node with two children now has just one child.
*
* We try to navigate upward till there are other nodes that can be
* compressed, when we reach the upper node which is not a key and has
* a single child, we scan the chain of children to collect the
* compressible part of the tree, and replace the current node with the
* new one, fixing the child pointer to reference the first non
* compressible node.
*
* Example of case "1". A tree stores the keys "FOO" = 1 and
* "FOOBAR" = 2:
*
*
* "FOO" -> "BAR" -> [] (2)
* (1)
*
* After the removal of "FOO" the tree can be compressed as:
*
* "FOOBAR" -> [] (2)
*
*
* Example of case "2". A tree stores the keys "FOOBAR" = 1 and
* "FOOTER" = 2:
*
* |B| -> "AR" -> [] (1)
* "FOO" -> |-|
* |T| -> "ER" -> [] (2)
*
* After the removal of "FOOTER" the resulting tree is:
*
* "FOO" -> |B| -> "AR" -> [] (1)
*
* That can be compressed into:
*
* "FOOBAR" -> [] (1)
*/
//尝试压缩
if (trycompress) {
debugf("After removing %.*s:\n", (int)len, s);
debugnode("Compression may be needed",h);
debugf("Seek start node\n");
/* Try to reach the upper node that is compressible.
* At the end of the loop 'h' will point to the first node we
* can try to compress and 'parent' to its parent. */
raxNode *parent;
//压缩时,需要先找到当前节点的父节点,在循环之后,h指向第一个我们可以压缩的节点并且parent指向父节点
while(1) {
parent = raxStackPop(&ts);
if (!parent || parent->iskey ||
(!parent->iscompr && parent->size != 1)) break;
h = parent;
debugnode("Going up to",h);
}
raxNode *start = h; /* Compression starting node. */
/* Scan chain of nodes we can compress. */
size_t comprsize = h->size;
int nodes = 1;
while(h->size != 0) {
raxNode **cp = raxNodeLastChildPtr(h);
memcpy(&h,cp,sizeof(h));
if (h->iskey || (!h->iscompr && h->size != 1)) break;
/* Stop here if going to the next node would result into
* a compressed node larger than h->size can hold. */
if (comprsize + h->size > RAX_NODE_MAX_SIZE) break;
nodes++;
comprsize += h->size;
}
if (nodes > 1) {
/* If we can compress, create the new node and populate it. */
size_t nodesize =
sizeof(raxNode)+comprsize+raxPadding(comprsize)+sizeof(raxNode*);
raxNode *new = rax_malloc(nodesize);
/* An out of memory here just means we cannot optimize this
* node, but the tree is left in a consistent state. */
if (new == NULL) {
raxStackFree(&ts);
return 1;
}
new->iskey = 0;
new->isnull = 0;
new->iscompr = 1;
new->size = comprsize;
rax->numnodes++;
/* Scan again, this time to populate the new node content and
* to fix the new node child pointer. At the same time we free
* all the nodes that we'll no longer use. */
comprsize = 0;
h = start;
while(h->size != 0) {
//将需要合并的节点合并到一个新的节点
memcpy(new->data+comprsize,h->data,h->size);
comprsize += h->size;
raxNode **cp = raxNodeLastChildPtr(h);
raxNode *tofree = h;
memcpy(&h,cp,sizeof(h));
//旧的节点在合并后释放
rax_free(tofree); rax->numnodes--;
if (h->iskey || (!h->iscompr && h->size != 1)) break;
}
debugnode("New node",new);
/* Now 'h' points to the first node that we still need to use,
* so our new node child pointer will point to it. */
//让新节点的子指针指向被删除节点的后面的节点
raxNode **cp = raxNodeLastChildPtr(new);
memcpy(cp,&h,sizeof(h));
/* Fix parent link. */
if (parent) {
//让被删除节点指向新节点地址
raxNode **parentlink = raxFindParentLink(parent,start);
memcpy(parentlink,&new,sizeof(new));
} else {
rax->head = new;
}
debugf("Compressed %d nodes, %d total bytes\n",
nodes, (int)comprsize);
}
}
raxStackFree(&ts);
return 1;
}
可以看到,remove操作相对于insert简化很多,remove只需要定位到当前层级,依次向上遍历看是否需要同时删除父节点,在删除后看是否需要合并子节点即可。
rax总结
从整个rax实现上看,由于需要覆盖所有情况,导致rax的增删操作相对复杂,每个操作函数也是相当的长,整体性能一般。
redis在rax的整个功能实现上是完整的,但是从构造上看并没有打算以后对rax加入极致的效率优化,在6中作为stream的stream ID存储,ACL安全策略等广泛使用。
